Links to official Saudi websites end with gov.sa
All links to official websites of government agencies in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia end with .gov.sa
Government websites use the HTTPS protocol for encryption and security.
Secure websites in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia use the HTTPS protocol for encryption.
Registered with the Digital Government Authority under number :
20250519510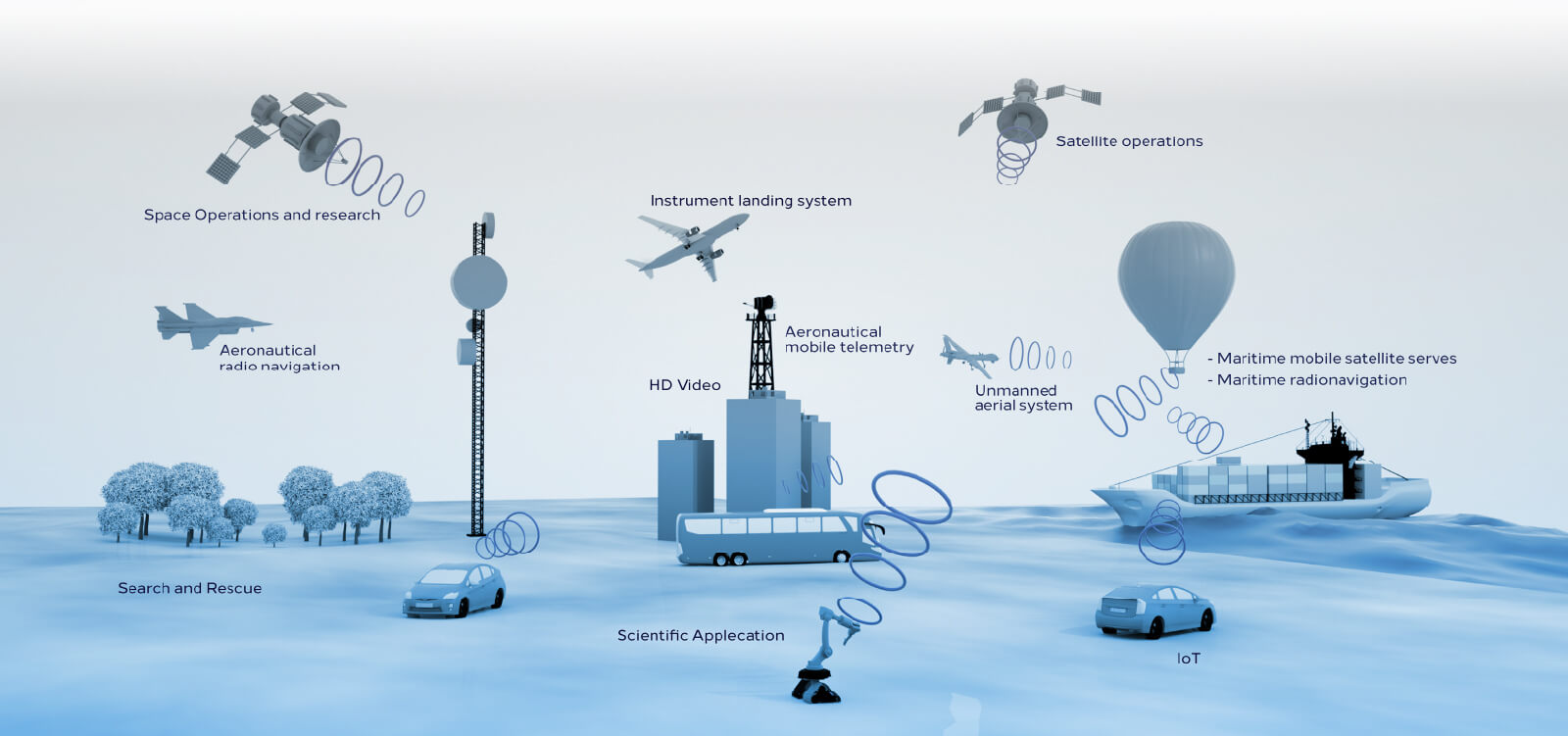
Air-borne
Air-borne is a heterogeneous networks that are engineered to utilize satellites, high-altitude platforms (HAPs), and low-altitude platforms (LAPs) to build communication access platforms. Furthermore, A2G is a special application of air-born that provide internet on civilian aircraft via terrestrial network.
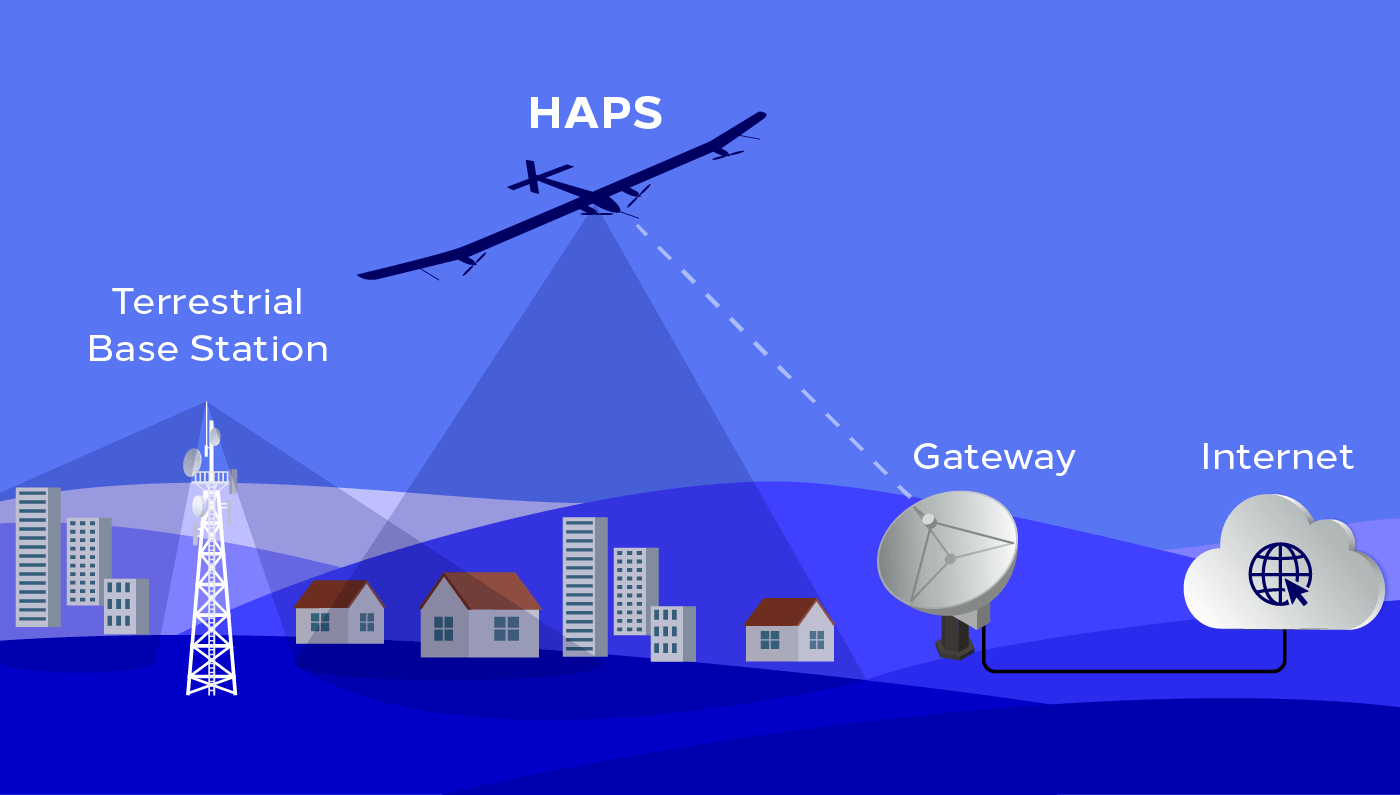
High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS)
HAPS are radio stations located on an object that floats at the stratosphere layer and at a specified, nominal, fixed point relative to the Earth, providing telecommunication services coverage over a wide geographical range, with high quality signal.
1 / 3
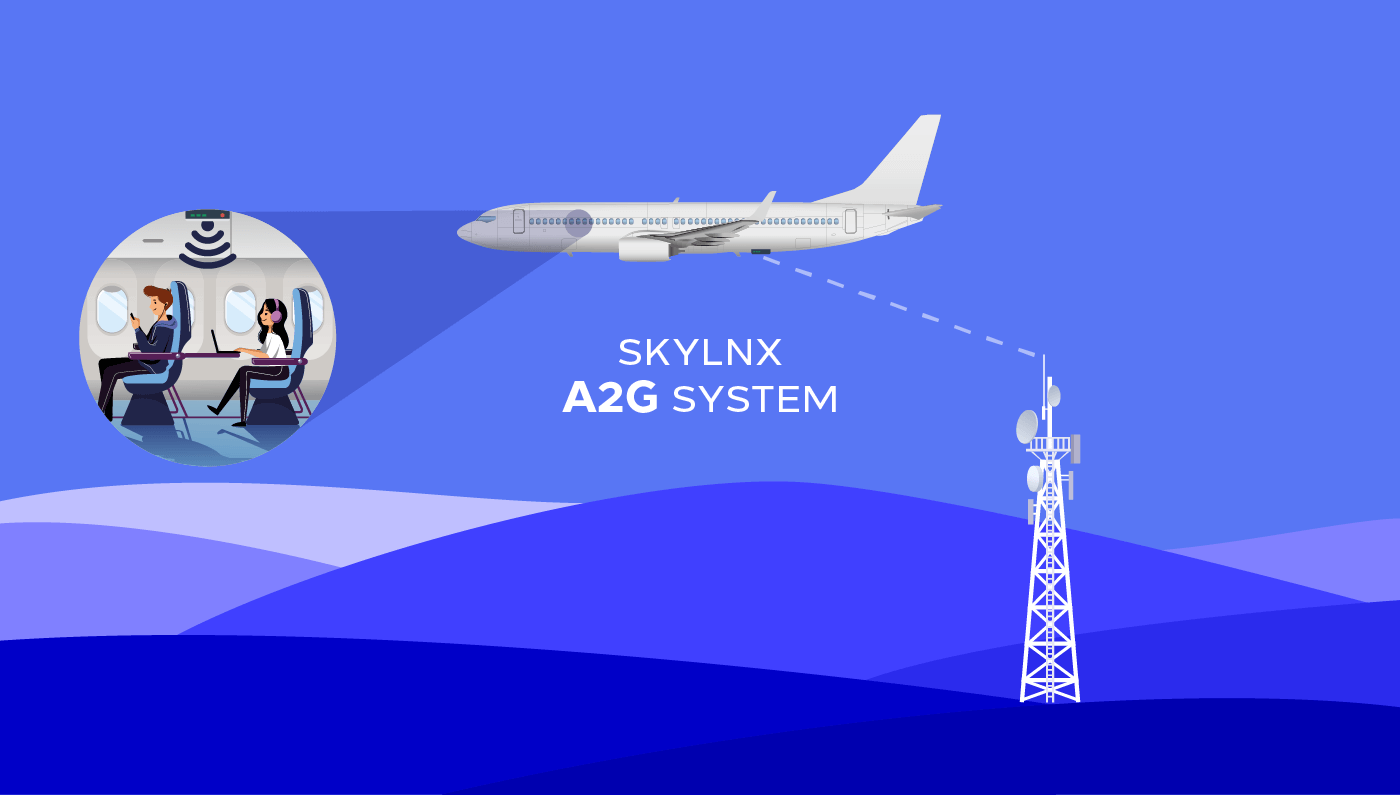
Air-to-Ground (A2G)
Air-to-Ground is a Two-way communication between aircraft and stations or locations on the surface of the earth.
The ground network consists of A2G base stations with skywards-pointing antennas optimized for airspace coverage, which create very large cells in the sky. Given that, unlike on the ground, radio signals can freely propagate.
2 / 3
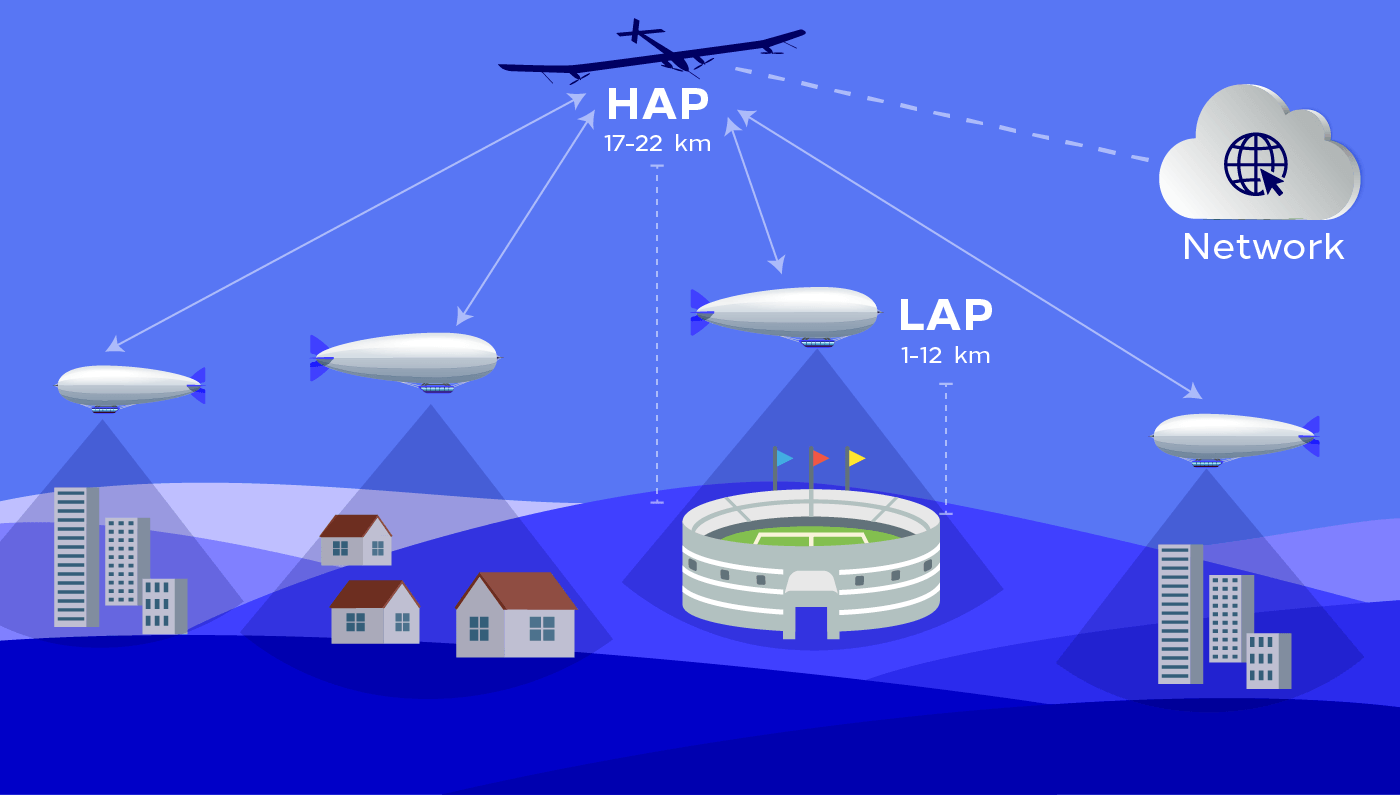
Low Altitude Platforms (LAPS)
A LAP is an object (may be a UAV or balloon) that have the capability of flying at low altitudes (e.g., a few hundreds of meters) for a sufficient endurance for completing a mission.
3 / 3
Table Matrix (LAPS vs HAPS)
| Performance | HAP | LAP |
|---|---|---|
| Footprint | Large | Small |
| Vulnerability to natural disasters | Reduced | Reduced |
| Overflight | Restricted | Restricted |
| Responsiveness and flexibility | Medium | Rapid |
| Communication persistence | Long | Short |
| Propagation delay | Short | Short |
| Broadcast/ multicast | Capable | Capable |
| Cost | Medium | Low |

